Discover the Power
of Wellbeing Partnership
Our Services
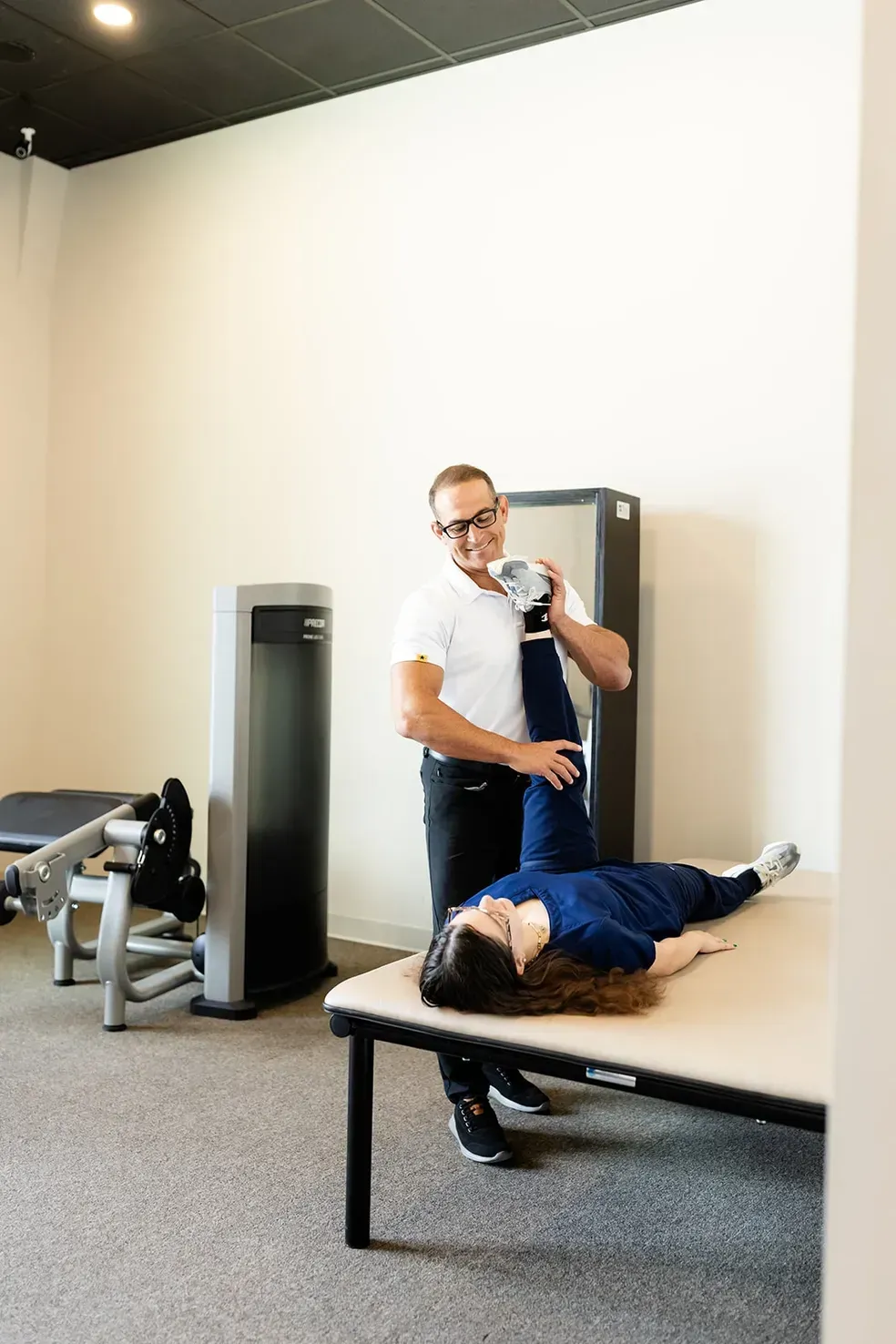
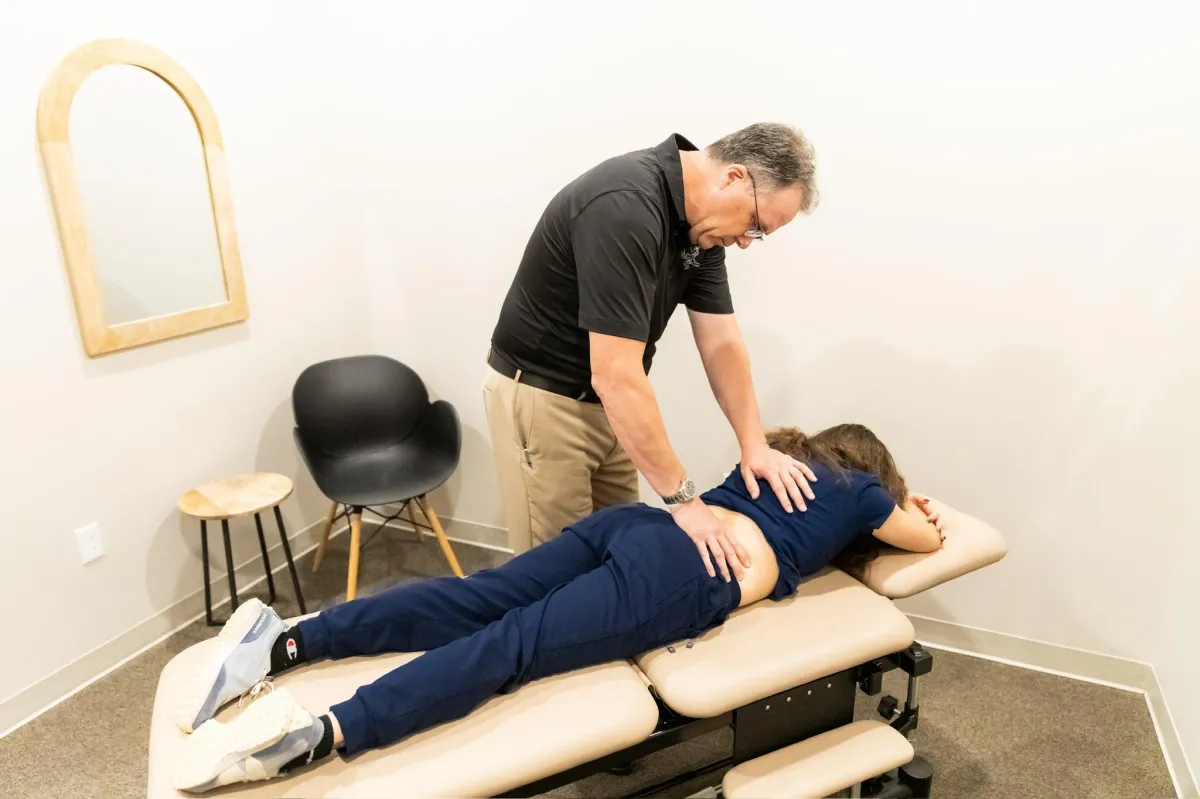
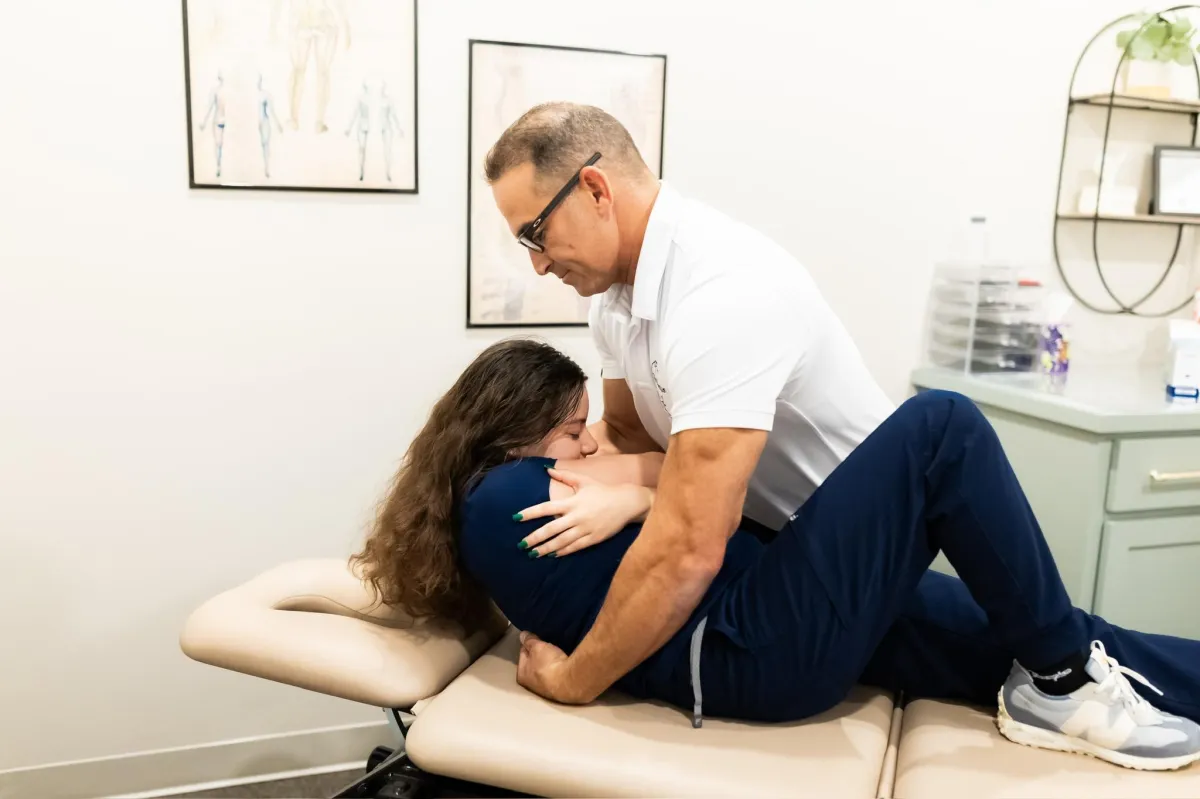
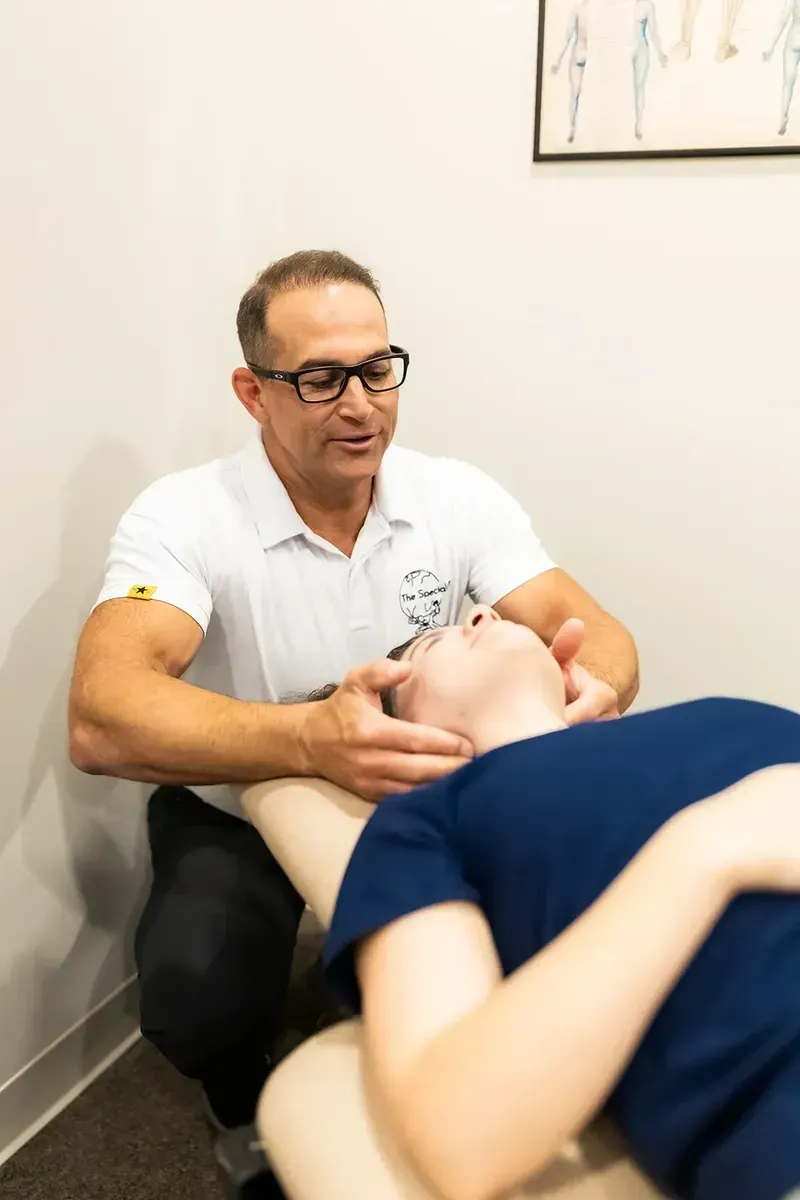
Integrative Movement
and Recovery Care
-Osteopathic Manual Therapy
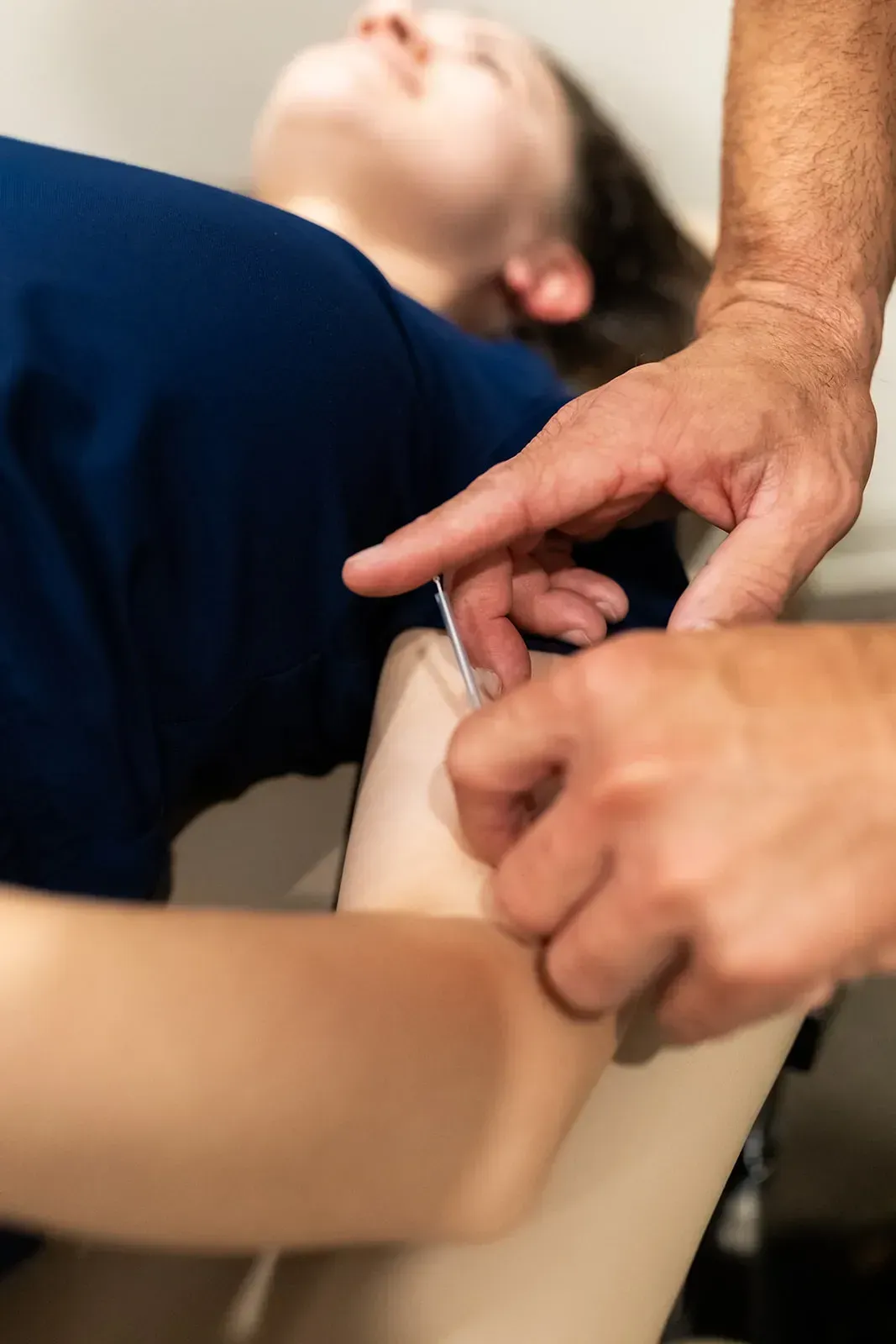
-Dry Needling
-Soft Tissue Mobilization
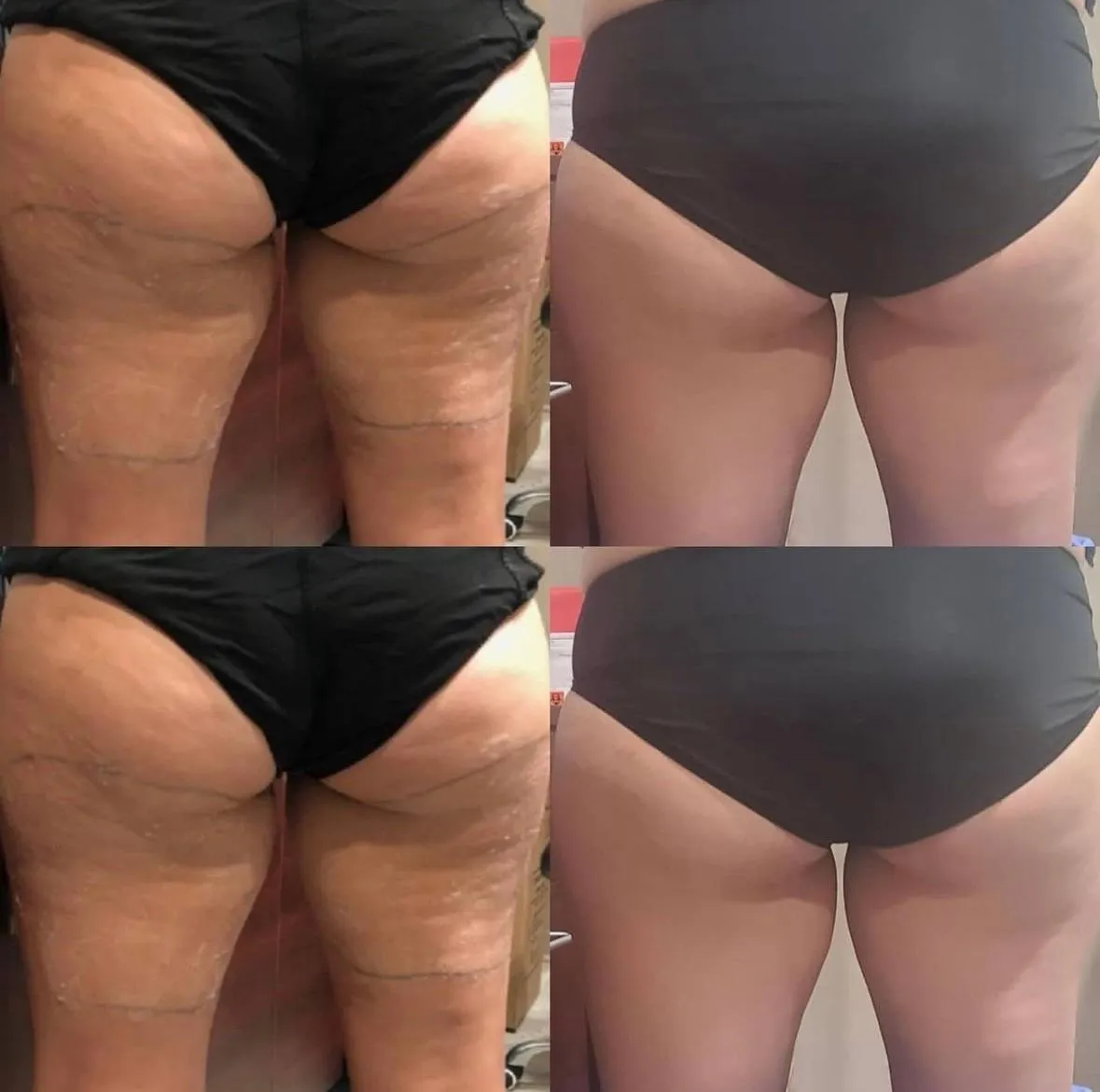
-Softwave (TRT) Shockwave Therapy
-Cupping & Scraping
-High Intensity Laser
-Advanced Exercise Sequencing
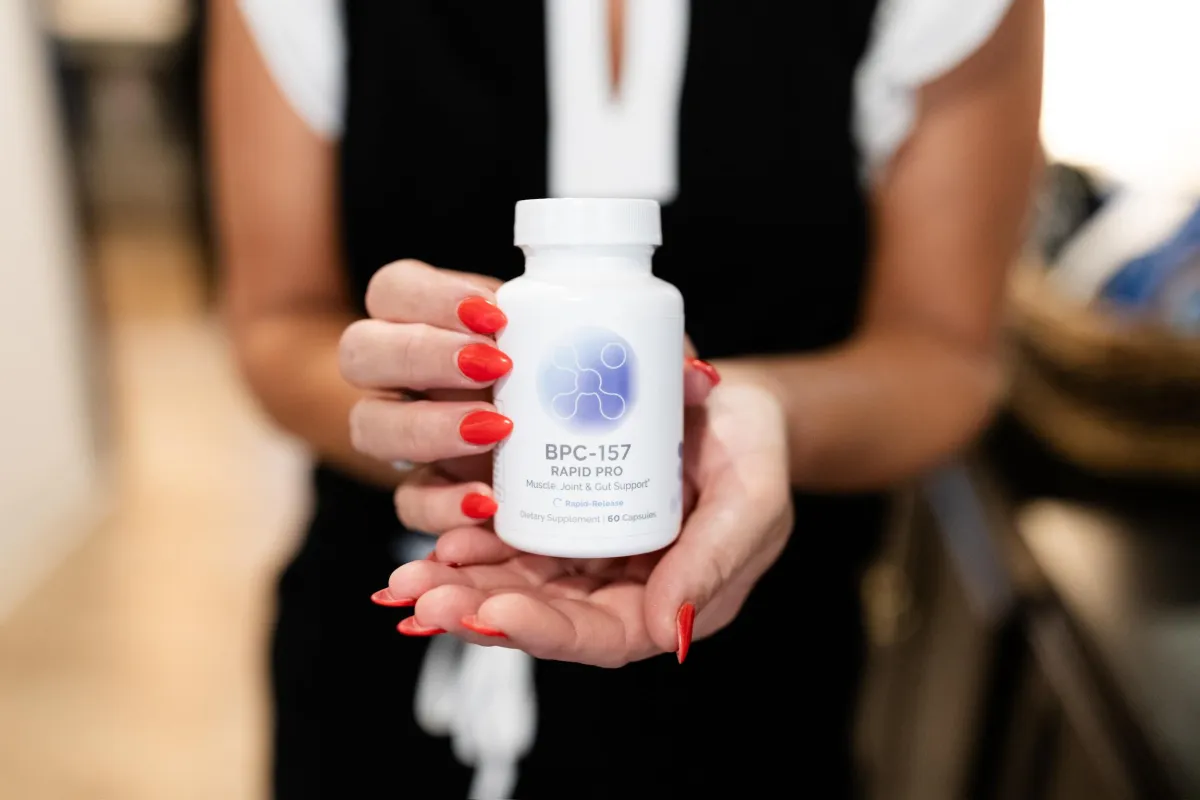
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
-Mesenchymal Stem Cell & Exosome Treatments
-Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy
Metabolic and
Longevity Medicine
-Metabolic Management
-Hormone Replacement
-IV Therapy
-Joint Injections
-Weight Management Programs
-Personalized Nutrition Plans
-Online Consultations
-Supplement Recommendations
-Nutritional Testing
-Body Composition Testing
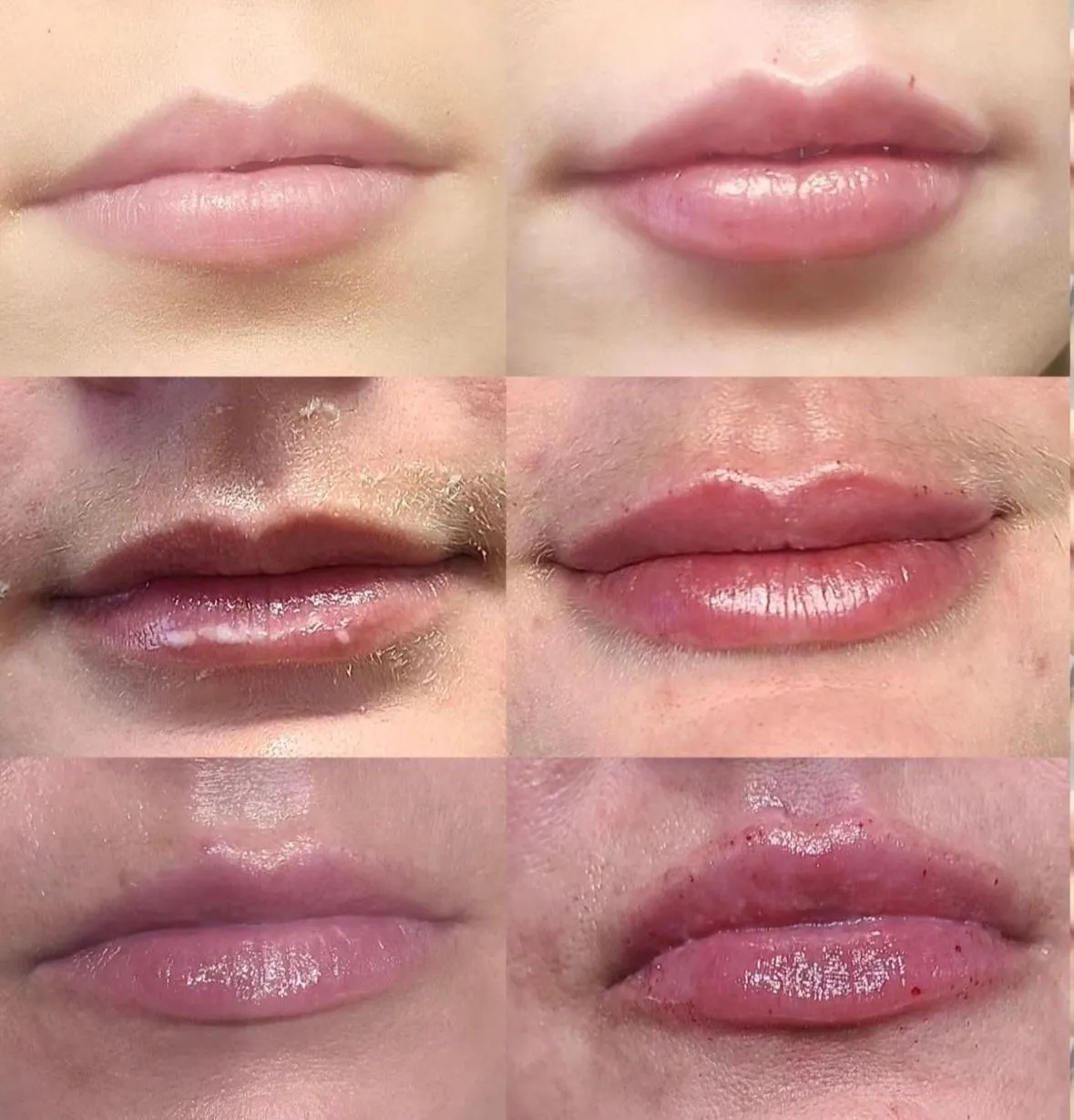
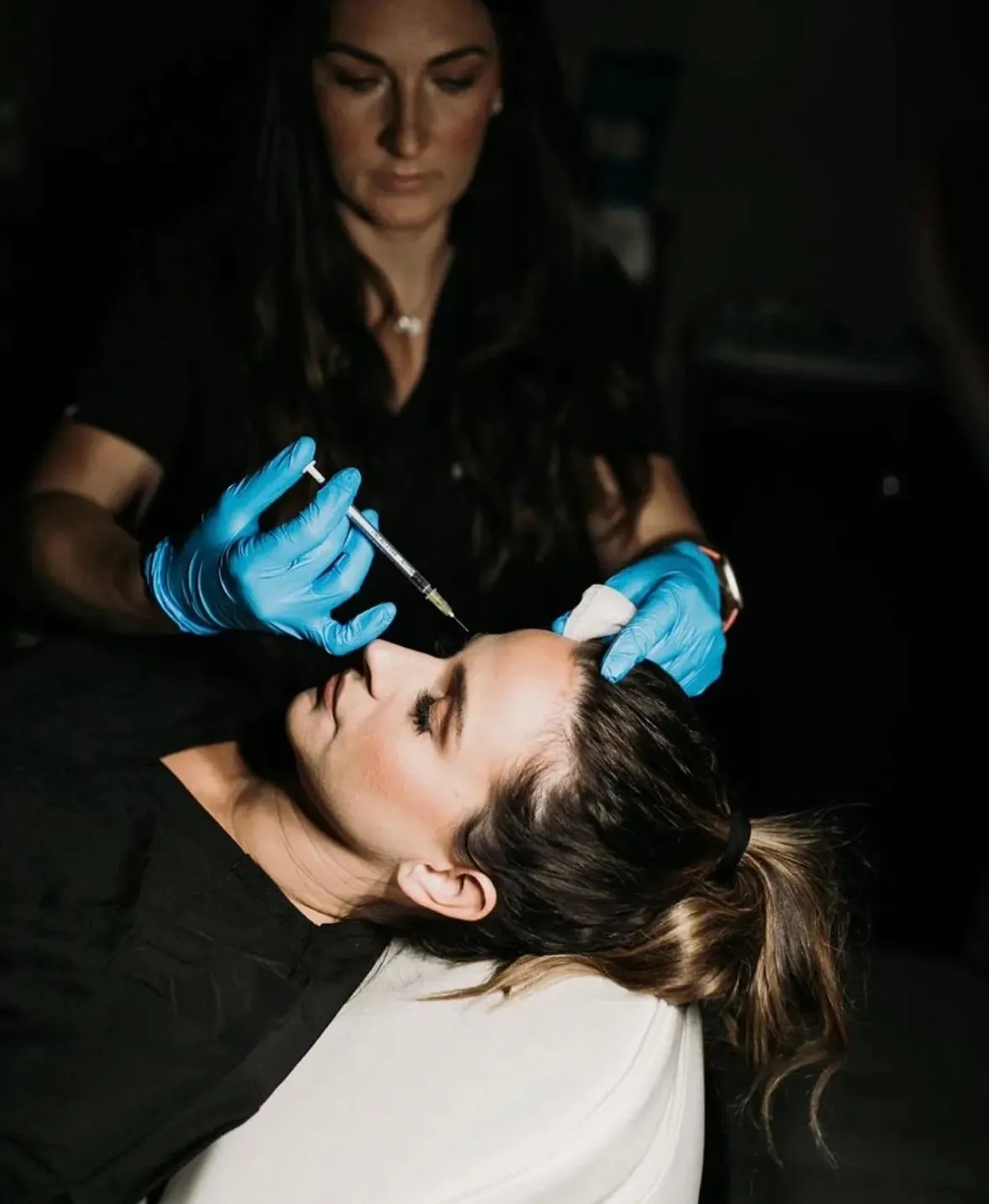
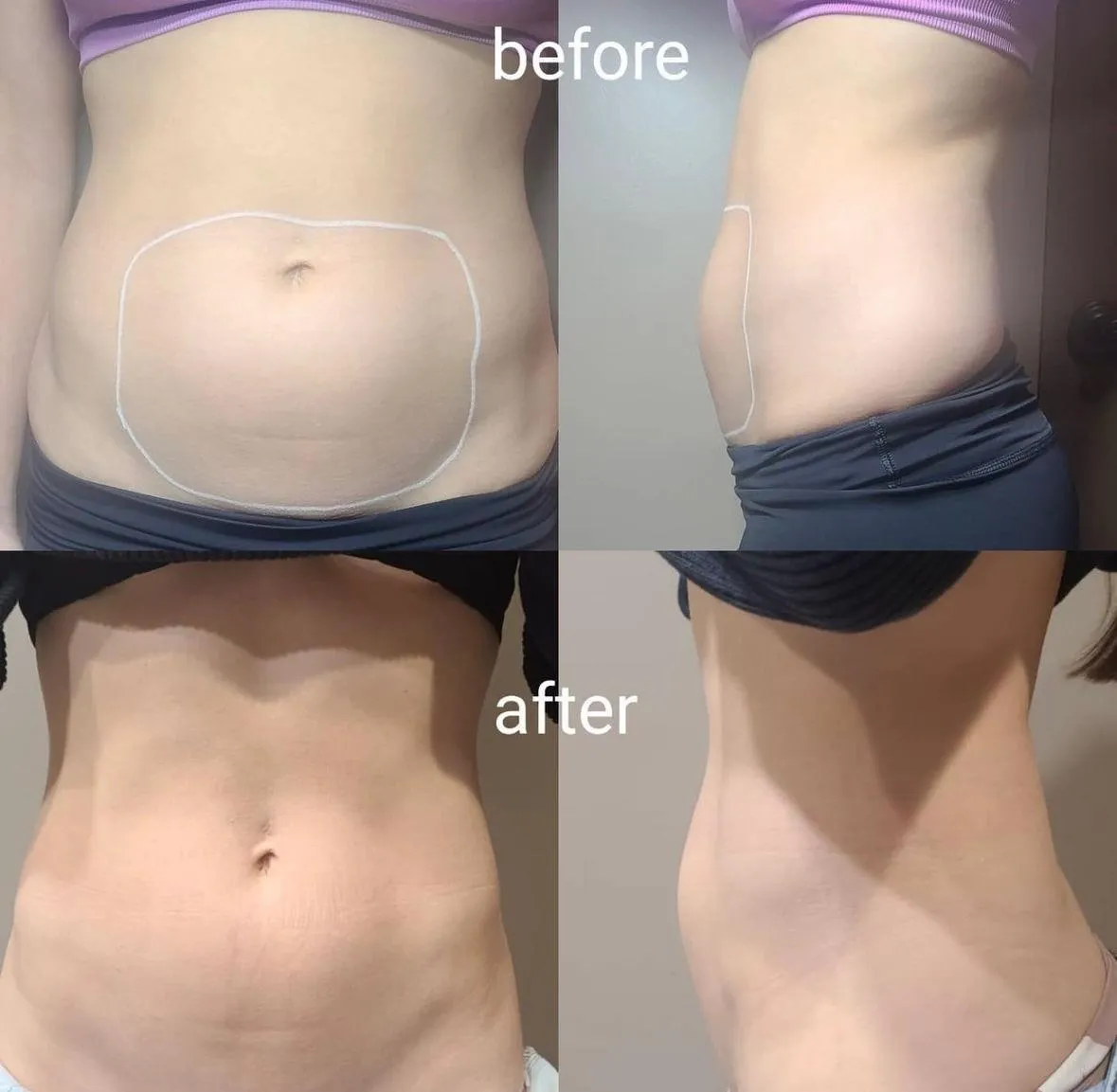
Modern Beauty Enhancements
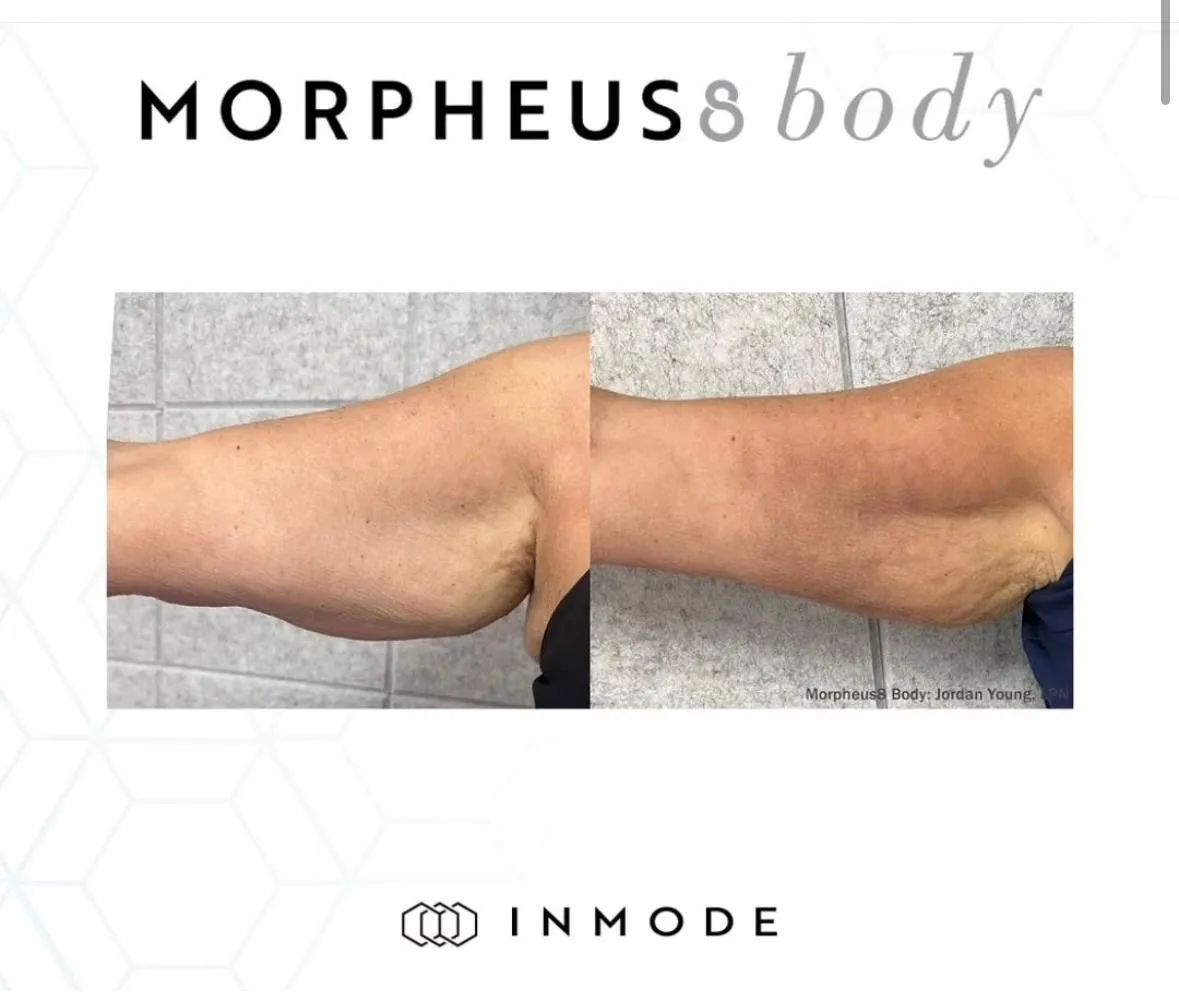
-Morpheus 8
-Botox & Dysport
-Dermal Fillers
-Exosome & Stem Cell
-Facial & Hair Treatments
-Kybella
-Sculptra
STILL NOT SURE?
Frequently Asked Questions
What services does your clinic offer?
We specialize in an integrative approach to health and performance, offering:
Physical Therapy – for recovery, mobility, and injury prevention
Regenerative Medicine – advanced, non-surgical options to support healing
Metabolic Management – customized plans for weight loss, energy, and overall health
DEXA Scans – precise body composition analysis for fitness, health, and progress tracking
SoftWave Therapy – shockwave treatment that promotes healing, reduces pain, and accelerates recovery
Do I need a referral to begin treatment?
No referral is required to get started. We welcome direct access appointments for most services. However, certain insurance plans may require a referral for physical therapy coverage—our team can help you check.
What is SoftWave Therapy and how does it work?
SoftWave is a non-invasive shockwave treatment that stimulates the body’s natural healing response. It increases circulation, reduces inflammation, and accelerates tissue repair—making it ideal for chronic pain, joint issues, and recovery support.
What is a DEXA scan and who should get one?
A DEXA scan measures your bone density and body composition (muscle, fat, and more). It’s perfect for anyone looking to track fitness progress, optimize health, monitor bone health, or guide weight management strategies.
How is Metabolic Management different from a regular diet plan?
Our Metabolic Management program is medically guided and tailored to your unique health needs. We focus on identifying metabolic dysfunction, supporting hormone balance, improving energy, and achieving sustainable results with science-backed strategies.
What can I expect on my first visit?
Your first visit includes a thorough consultation, evaluation, and a clear explanation of the best treatment path for your goals. Depending on your needs, this may include physical assessments, health screenings, or a DEXA scan.
Do you accept insurance?
Yes, we accept many insurance plans for eligible services, especially physical therapy. For services not covered by insurance, we offer transparent pricing and flexible payment options. We also offer the ability to bill through The Specialist account for added convenience.
How do I schedule an appointment?
Request an appointment on our contact page, call our front desk, or stop by in person. Our team will match you with the right provider and service based on your goals.
What makes your clinic different?
We blend the best of modern medicine, wellness, and performance care in one location. Whether you're recovering from injury, optimizing your health, or preventing future issues, our whole-body approach and cutting-edge tools deliver long-term results.
What exactly does physical therapy involve, and how can it help me?
Physical therapy involves targeted exercises, manual techniques, and personalized treatment plans designed to improve mobility, reduce pain, and restore physical function. It’s an effective approach to recovering from injury, managing chronic conditions, and enhancing your overall quality of life.
How can I tell if physical therapy is the right choice for my condition?
If you’re struggling with pain, reduced movement, or difficulty in performing daily tasks due to an injury, surgery, or chronic issue, physical therapy may be beneficial. Our therapists can provide a consultation to assess your needs and determine if therapy is suitable for you.
Is my privacy protected during physical therapy sessions?
Absolutely. Your privacy and safety are top priorities, and all therapy sessions are conducted in a secure, confidential environment. We follow strict guidelines to ensure that your personal and health information remains private.
How many sessions does it usually take to see improvement with physical therapy?
Improvement times can vary based on individual goals and the nature of your condition. Some people notice progress after just a few sessions, while others may require several weeks of therapy. Your therapist will create a customized plan and monitor your progress to help you achieve the best results.